Munich old map
You can find on this page the Munich old map to print and to download in PDF. The Munich historical map and the vintage map of Munich present the past and evolutions of the city of Munich in Bavaria - Germany.
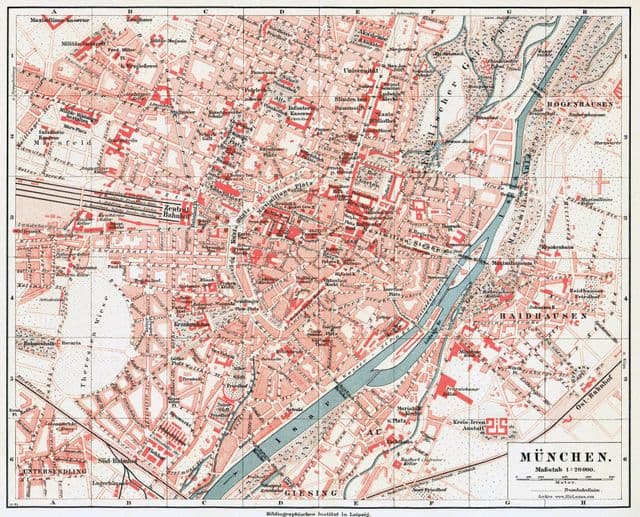
Munich historical map
The Munich old map shows evolutions of Munich city. This historical map of Munich will allow you to travel in the past and in the history of Munich in Bavaria - Germany. The Munich ancient map is downloadable in PDF, printable and free.
The monks presence dated back to the 8th century , although settlement in the historical Munich area can be traced back to the late neolithic. To force traders to use his bridge (and charge them for doing so) Henry also destroyed a nearby bridge owned by bishop Otto von Freising ( Freising ). Subsequently the bishop and Henry quarreled about the city before Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa at an Imperial Diet held in Augsburg in 1158 as its shown in Munich historical map. This sanctioned Henry spoliation, and awarded an annual compensation for the bishop, and also confirmed Munich trading and currency rights. Almost two decades later in 1175 Munich was officially granted city status and received fortification.
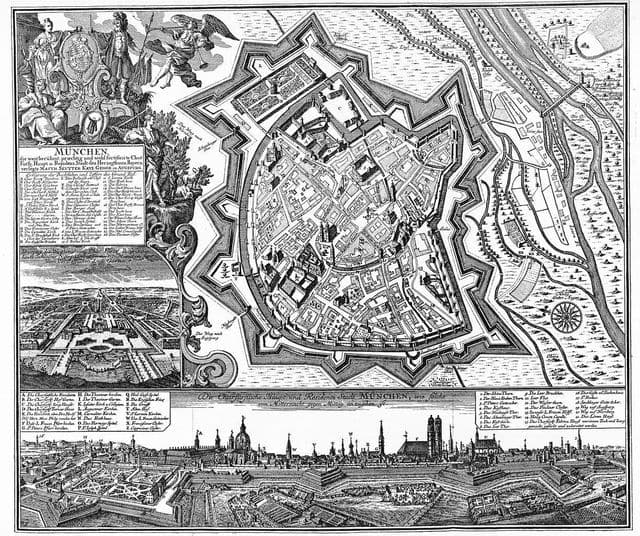
Munich vintage map
The Munich vintage map give a unique insight into the history and evolution of Munich city. This vintage map of Munich with its antique style will allow you to travel in the past of Munich in Bavaria - Germany. The Munich vintage map is downloadable in PDF, printable and free.
When Bavaria was reunited in 1506 Munich became capital of the whole of vintage Bavaria. The arts and politics became increasingly influenced by the court. During the 16th century Munich was a center of the German counter reformation , and also of renaissance arts. Duke Wilhelm V commissioned the Jesuit Michaelskirche , which became a center for the counter-reformation, and also built the Hofbräuhaus for brewing brown beer in 1589 as its mentioned in Munich vintage map. The Catholic League was founded in Munich in 1609. In 1623 during the Thirty Years War Munich became electoral residence when Maximilian I, Duke of Bavaria was invested with the electoral dignity but in 1632 the city was occupied by Gustav II Adolph of Sweden . When the bubonic plague broke out in 1634 and 1635 about one third of the population died.
